This is an overview of trends and technologies in radiologyartificial intelligence (AI)applications in 2021. Views were shared by 11 radiologists using AI and industry leaders, which include:
•Randy Hicks, M.D.,MBA, radiologist and CEO of Reginal Medical Imaging (RMI), and an iCAD Profound AI user.
•Prof. Dr. Thomas Frauenfelder, University of Zurich, Institute for Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, and Riverain AI user.
•Amy Patel, M.D., medical director of Liberty Hospital Women’s Imaging, assistant professor of radiology at UMKC, and user of Kios AI for breast ultrasound.
•Sham Sokka, Ph.D., vice president and head of innovation, precision diagnosis, Philips Healthcare.
•Ivo Dreisser, Siemens Healthineers, global marketing manager for the AI Rad Companion.
•Bill Lacey,vice president of medical informatics, Fujifilm Medical Systems USA.
•Karley Yoder,vice president and general manager, artificial intelligence, GE Healthcare.
•Georges Espada,head of Agfa Healthcare digital and computed radiography business unit.
•Pooja Rao, head of research and development and co-founder of Qure.ai.
•Jill Hamman,world-wide marketing manager at Carestream Health.
•Sebastian Nickel, Siemens Healthineers, global product manager for the AI Pathway Companion.
There has been a change in attitudes about AI on the expo floor at theRadiological Society of North America(RSNA) over the last two years. AI conversations were originally 101 level and discussed how AI technology could be trained to sort photos of dogs and cats. However, in 2020, with numerous FDA approvals for various AI applications, the conversations at RSNA, and industry wide, have shifted to that of accepting the validity of AI. Radiologists now want to discuss how a specific AI algorithm is going to help them save time, make more accurate diagnoses and make them more efficient.
随着人工智能的成熟程度越来越高,这项技术得到了更广泛的应用,使用人工智能的放射科医生表示,人工智能给他们的诊断带来了额外的信心,甚至可以帮助那些在他们被要求阅读的考试类型方面可能不是深入专家的读者。
With a myriad of new AI apps gaining regulatory approval from scores of imaging vendors, the biggest challenge for getting this technology into hospitals is an easy to integrate format. This has led to several vendors creating AI app stores. These allow AI apps to integrate easily into radiology workflows because the apps are already integrated as third-party software into a larger radiology vendors' IT platform.
There are now hundreds of AI applications that do a wide variety of analysis, from data analytics, image reconstruction, disease and anatomy identification, automating measurements and advanced visualization. The AI applications can be divided into 2 basic types — AI to improve workflow, and AI for clinical decision support, such as diagnostic aids.
On the workflow side, several vendors are leveraging AI to pull together all of a patients' information, prior exams and reports in one location and to digest the information so it is easier for the radiologist to consume. Often the AI pulls only data and priors that relate to a specific question being asked, based on the imaging protocol used for the exam. One example of this is the Siemens Healthineers AI Clinical Pathway and Siemens AI integrations with PACS to automate measurements and advanced visualization.
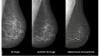
AI is also helping simplify complex tasks and help reduce the reading time on involved exams. One example of this is in 3-D breast tomosythesis with hundreds of images, which is rapidly replacing 2-D mammography, which only produces 4 images. Another example is automated image reconstruction algorithms to significantly reduce manual work. AI also is now being integrated directly into several vendors' imaging systems to speed workflow and improve image quality.
Vendors say AI is here to stay. They explain the future of AI will be automation to help improve image quality, simplify manual processes, improved diagnostic quality, new ways to analyze data, and workflow aids that operate in the background as part of a growing number of software solutions.
Several vendors at RSNA 2020 noted that AI's biggest impact in the coming years will be its ability to augment and speed the workflow for the small number of radiologists compared to the quickly growing elder patient populations worldwide. There also are applications in rural and developing countries were there are very low numbers of physicians or specialists.
Related AI in Medical Imaging Content:
AI Outperforms Humans in Creating Cancer Treatments, But Do Doctors Trust It?
VIDEO: Artificial Intelligence For MRI Helps Overcome Backlog of Exams Due to COVID
How AI is Helping the Fight Against Breast Cancer
VIDEO: Use of Artificial Intelligence in Nuclear Imaging
3 High-impact AI Market Trends in Radiology at RSNA 2019
Photo Gallery of New Imaging Technologies at RSNA 2019
VIDEO: Editors Choice of the Most Innovative New Radiology Technology at RSNA 2019
Study Reveals New Comprehensive AI Chest X-ray Solution Improves Radiologist Accuracy
VIDEO: Real-world Use of AI to Detect Hemorrhagic Stroke
The Radiology AI Evolution at RSNA 2019
Eliminating Bias from Healthcare AI Critical to Improve Health Equity
VIDEO: FDA Cleared Artificial Intelligence for Immediate Results of Head CT Scans
Building the Future of AI Through Data
WEBINAR: Do More, Perform Better: Delivering Clinical Quality through Advanced Radiology and Artificial Intelligence
Integrating Artificial Intelligence in Treatment Planning
Selecting an AI Marketplace for Radiology: Key Considerations for Healthcare Providers
Artificial Intelligence Improves Accuracy of Breast Ultrasound Diagnoses
Artificial Intelligence Greatly Speeds Radiation Therapy Treatment Planning
WEBINAR: Building the Bridge - How Imaging AI is Delivering Clinical Value Across the Care Continuum
AI in Medical Imaging Market to Reach $1.5B by 2024
VIDEO: AI-Assisted Automatic Ejection Fraction for Point-of-Care Ultrasound
5 Trends in Enterprise Imaging and PACS Systems
VIDEO: Artificial Intelligence to Automate CT Calcium Scoring and Radiomics
Scale AI in Imaging Now for the Post-COVID Era
VIDEO: Integrating Artificial Intelligence Into Radiologists Workflow
Northwestern Medicine Introduces Artificial Intelligence to Improve Ultrasound Imaging
Find more artificial intelligence news and video