Yael Eshet, M.D., MSc, a diagnostic radiology specialist atSheba Medical Centerin Israel, was the lead author on a recent study that showedCOVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2)vaccine adenopathy can persist more than 6 weeks. This swelling of lymph nodes is similar to what is seen cancer and infections and the new findings show it can last longer than 7-10 weeks. The current recommended time people should delay medical imaging is 6 weeks after receiving a COVID vaccine to avoid a misdiagnosis,[2] but this new study shows there is increased inflammation shown on PET-CT imaging for much longer.
These were the findings in theRadiologypublished study"Prevalence of Increased FDG PET/CT Axillary Lymph Node Uptake Beyond 6 Weeks after mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination."[1]
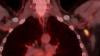
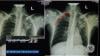
Researchers using fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)-positron emission tomography (PET)have found increased FDG uptake in the lymph nodes of patients 7-10 weeks past their second mRNA-based Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccination. This new information indicates a persistent immune response that could be mistaken on imaging exams for serious conditions like lymphoma over a much longer period of time.
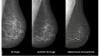
Recent recommendations for post-vaccine lymphadenopathy advise scheduling routine imaging, such as screening mammography, before, or at least 6 weeks after, the final vaccination dose to eliminate false positive results. However, this new research showed that avid axillary lymph node uptake was present beyond 6 weeks after the second vaccination in more than 29% of the patients in the study cohort.
The authors stated “This study shows that avid axillary lymph node uptake on FDG PET/CT can be detected in more than a quarter of our patient population even beyond 6 weeks after the second dose of the mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccination. Compared to a previous study showing normalization of FDG uptake within 40 days of receiving an inactivated H1N1 influenza vaccine, we found uptake persistence even at 70 days. Physicians should be aware of this potential pitfall.”
Some images in this video are from anotherRadiologystudy, which showed PET tracer uptake at the COVID vaccine injection site and other examples of axillary adenopathy.[3]
Related COVID Vaccine Axillary Adenapathy Content:
COVID-19 Vaccine Can Cause False Positive Cancer Diagnosis
Help Spread Awareness of Potential COVID-19 Vaccine Imaging Side-effects
视频:COVID Vaccine May Cause Enlarged Lymph Nodes on Mammograms— Interview with Constance "Connie" Lehman, M.D.
COVID-19 Vaccination Axillary Adenopathy Detected During Breast Imaging
PHOTO GALLERY: How COVID-19 Appears on Medical Imaging
CMS Now Requires COVID-19 Vaccinations for Healthcare Workers by January 4
Find more radiology related COVID content
References:
1.Yael Eshet, Noam Tau1, Yousef Alhoubani, Nayroz Kanana, Liran Domachevsky, Michal Eifer。mRNA COVID-19疫苗接种6周后FDG PET/CT腋窝淋巴结摄取增加的发生率放射学。Published Online:Apr 27 2021https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2021210886.
2.Constance D. Lehman, Leslie R. Lamb, and Helen Anne D'Alessandro. Mitigating the Impact of Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Vaccinations on Patients Undergoing Breast Imaging Examinations: A Pragmatic Approach American Journal of Roentgenology. 10.2214/AJR.21.25688.
3.可以Özütemiz, Luke A. Krystosek, An L. Church, Anil Chauhan, Jutta M. Ellermann, evdio Domingo-Musibay, Daniel Steinberger。COVID-19疫苗接种者的淋巴结病:肿瘤患者的诊断困境。放射学。Published Online:Feb 24 2021https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2021210275.