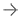Getty Images
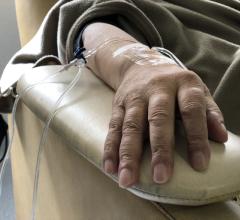
June 15, 2021 — The impact of deployingartificial intelligence(AI) forradiation cancer therapyin a real-world clinical setting has been tested byPrincess Margaretresearchers in a unique study involving physicians and their patients.
A team of researchers directly compared physician evaluations of radiation treatments generated by an AI machine learning (ML) algorithm to conventional radiation treatments generated by humans.
They found that in the majority of the 100 patients studied, treatments generated using ML were deemed to be clinically acceptable for patient treatments by physicians.
Overall, 89% of ML-generated treatments were considered clinically acceptable for treatments, and 72% were selected over human-generated treatments in head-to-head comparisons to conventional human-generated treatments.
Moreover, the ML radiation treatment process was faster than the conventional human-driven process by 60%, reducing the overall time from 118 hours to 47 hours. In the long term this could represent a substantial cost savings through improved efficiency, while at the same time improving quality of clinical care, a rare win-win.
The study also has broader implications for AI in medicine.
While the ML treatments were overwhelmingly preferred when evaluated outside the clinical environment, as is done in most scientific works, physician preferences for the ML-generated treatments changed when the chosen treatment, ML or human-generated, would be used to treat the patient.
In that situation, the number of ML treatments selected for patient treatment was significantly reduced issuing a note of caution for teams considering deploying inadequately validated AI systems.
Results by the study team led by Drs. Chris McIntosh, Leigh Conroy, Ale Berlin, and Tom Purdie are published inNature Medicine, June 3, 2021.
"We have shown that AI can be better than human judgement for curative-intent radiation therapy treatment. In fact, it is amazing that it works so well," saidChris McIntosh, Ph.D., Scientist at thePeter Munk Cardiac Centre, Techna Institute, and chair of Medical Imaging and AI at the Joint Department of Medical Imaging and University of Toronto.
“一个主要发现是,当你在临床环境中与模拟环境进行比较时,会发生什么。”
AddedTom Purdie, Ph.D., Medical Physicist, Princess Margaret Cancer Centre: "There has been a lot of excitement generated by AI in the lab, and the assumption is that those results will translate directly to a clinical setting. But we sound a cautionary alert in our research that they may not.
"Once you put ML-generated treatments in the hands of people who are relying upon it to make real clinical decisions about their patients, that preference towards ML may drop. There can be a disconnect between what's happening in a lab-type of setting and a clinical one." Purdie is also an Associate Professor, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Toronto.
In the study, treating radiation oncologists were asked to evaluate two different radiation treatments - either ML or human-generated ones - with the same standardized criteria in two groups of patients who were similar in demographics and disease characteristics.
The difference was that one group of patients had already received treatment so the comparison was a 'simulated' exercise. The second group of patients were about to begin radiation therapy treatment, so if AI-generated treatments were judged to be superior and preferable to their human counterparts, they would be used in the actual treatments.
肿瘤学家并不知道放射治疗是由人还是机器设计的。人类产生的治疗是由专门的放射治疗师根据正常协议为每个患者单独创建的。相比之下,每一种ML疗法都是由计算机算法开发的,该算法基于一个高质量的、同行评议的放疗计划数据库,该数据库来自玛格丽特公主医院之前治疗过前列腺癌的99名患者。
对于每个新患者,ML算法自动识别数据库中最相似的患者,使用从数千个患者图像特征中学习到的相似度指标,并划定目标和健康器官,这是放疗治疗过程的标准组成部分。根据ML模型,从数据库中最相似的患者中推断出一个新患者的完整治疗。
Although ML-generated treatments were rated highly in both patient groups, the results in the pre-treatment group diverged from the post-treatment group.
In the group of patients that had already received treatment, the number of ML-generated treatments selected over human ones was 83%. This dropped to 61% for those selected specifically for treatment, prior to their treatment.
"In this study, we're saying researchers need to pay attention to a clinical setting," said Purdie. "If physicians feel that patient care is at stake, then that may influence their judgement, even though the ML treatments are thoroughly evaluated and validated."
Leigh Conroy, Ph.D., Medical Physicist at Princess Margaret, points out that following the highly successful study, ML-generated treatments are now used in treating the majority of prostate cancer patients at Princess Margaret.
That success is due to careful planning, judicious stepwise integration into the clinical environment, and involvement of many stakeholders throughout the process of establishing a robust ML program, she explains, adding that the program is constantly refined, oncologists are continuously consulted and give feedback, and the results of how well the ML treatments reflect clinical accuracy are shared with them.
"We were very systematic in how we integrated this into the clinic at Princess Margaret," saidAle Berlin, M.D., Clinician-Scientist and Radiation Oncologist at Princess Margaret. "To build this novel software, it took about six months, but to get everyone on board and comfortable with the process, it took more than two years. Vision, audacity and tenacity are key ingredients, and we are fortunate at Princess Margaret to have leaders across disciplines that embody these attributes." Berlin is also an Assistant Professor, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Toronto.
The success for launching a study of this calibre relied heavily on the commitment from the entire genitourinary radiation cancer group at Princess Margaret, including radiation oncologists, medical physicists, and radiation therapists. This was a large multidisciplinary team effort with the ultimate goal for everyone to improve radiation cancer treatment for patients at Princess Margaret.
该团队还将研究范围扩大到其他癌症部位,包括肺癌和兽性癌症,目的是减少心脏毒性,这是治疗的一种可能的副作用。
For more information:www.


 August 10, 2022
August 10, 2022